News
In short-term packaging projects such as promotions, seasonal campaigns, and channel-specific releases, label content often changes frequently. Examples include campaign codes, channel marks, batch numbers, and temporary notices.
These scenarios are defined by frequent changes, multiple versions, and short lifecycle labels. Print and apply labeling machines operate here mainly through basic technical workflow control rather than extreme production speed.
Below is a practical, process-level explanation.
1️⃣ Template-based label switching
Short campaign labels are usually managed with fixed templates plus variable fields.
Typical setup:
Multiple label templates created
Each campaign uses one template
Layout remains fixed
Variable fields are reserved
Operators switch templates
Through HMI or software menu
Technically, this is simply loading different label format files, not redesigning labels each time.
2️⃣ Variable field replacement
Most campaign label changes affect only certain fields:
Campaign codes
Channel IDs
Dates and batches
Serial numbers
QR contents
Print and apply systems support variable data printing. Data sources usually include:
Host system data
Scanner input
Manual entry
Only defined fields are replaced while layout stays unchanged.
3️⃣ Trigger-based printing control
Short campaign packaging often requires print-after-confirmation logic. Common triggers include:
Scan-to-print
Weighing signal
Button confirmation
Order signal from system
Technically this is signal-triggered printing:
Signal present → print
No signal → wait
This prevents unused labels from being printed in advance.
4️⃣ Basic queue and cache handling
Label order problems can appear in small mixed batches. Most systems use simple print queues:
Data enters queue in order
Labels print in order
Cache can be cleared if needed
Typical operator actions before switching campaign versions:
Clear buffer
Reload template
Print one test label
This is standard operating procedure rather than advanced control logic.
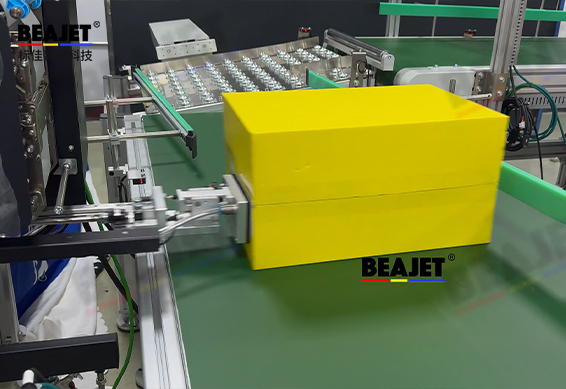
5️⃣ Mechanical adjustment for different packages
Short campaigns may involve different package types:
Cartons
Color boxes
Poly bags
Wrapped packs
Machines adapt mainly through basic adjustments:
Height adjustment
Apply angle adjustment
Switching tamp/blow/roll modes
These are mechanical and parameter adjustments, not complex modifications.
6️⃣ Common on-site switching workflow
Typical switching steps in campaign packaging:
Select template
Update variable rules
Clear print buffer
Print test label
Run small trial batch
Start full run
This is primarily workflow discipline, not high technical complexity.
In short-term campaign packaging, print and apply labeling machines function through template control, variable data replacement, trigger logic, and basic mechanical adjustment.
In real deployments, Hangzhou Beajet Digital Technology Co., Ltd. systems are usually configured around these basic mechanisms so operators can complete campaign label switching using standard operating steps.